---
description: Understand how to diagnose and troubleshoot Docker Desktop, and how to
check the logs.
keywords: Linux, Mac, Windows, troubleshooting, logs, issues, Docker Desktop
toc_max: 2
title: Troubleshoot Docker Desktop
linkTitle: Troubleshoot and diagnose
aliases:
- /desktop/linux/troubleshoot/
- /desktop/mac/troubleshoot/
- /desktop/windows/troubleshoot/
- /docker-for-mac/troubleshoot/
- /mackit/troubleshoot/
- /windows/troubleshoot/
- /docker-for-win/troubleshoot/
- /docker-for-windows/troubleshoot/
- /desktop/troubleshoot/overview/
- /desktop/troubleshoot/
tags: [ Troubleshooting ]
weight: 10
---
This page contains information on how to diagnose and troubleshoot Docker Desktop, and how to check the logs.
> [!WARNING]
>
> If you're experiencing malware detection issues on Mac, follow the steps documented in [docker/for-mac#7527](https://github.com/docker/for-mac/issues/7527).
## Troubleshoot menu
To navigate to **Troubleshoot** either:
- Select the Docker menu Docker menu {{< inline-image src="../../images/whale-x.svg" alt="whale menu" >}} and then **Troubleshoot**.
- Select the **Troubleshoot** icon near the top-right corner of Docker Dashboard.
The **Troubleshooting** menu contains the following options:
- **Restart Docker Desktop**.
- **Reset Kubernetes cluster**. Select to delete all stacks and Kubernetes resources. For more information, see [Kubernetes](/manuals/desktop/settings-and-maintenance/settings.md#kubernetes).
- **Clean / Purge data**. This option resets all Docker data without a
reset to factory defaults. Selecting this option results in the loss of existing settings.
- **Reset to factory defaults**: Choose this option to reset all options on
Docker Desktop to their initial state, the same as when Docker Desktop was first installed.
If you are a Mac or Linux user, you also have the option to **Uninstall** Docker Desktop from your system.
## Diagnose
> [!TIP]
>
> If you do not find a solution in troubleshooting, browse the GitHub repositories or create a new issue:
>
> - [docker/for-mac](https://github.com/docker/for-mac/issues)
> - [docker/for-win](https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues)
> - [docker/for-linux](https://github.com/docker/for-linux/issues)
### Diagnose from the app
1. From **Troubleshoot**, select **Get support**. This opens the in-app Support page and starts collecting the diagnostics.
2. When the diagnostics collection process is complete, select **Upload to get a Diagnostic ID**.
3. When the diagnostics are uploaded, Docker Desktop prints a diagnostic ID. Copy this ID.
4. Use your diagnostics ID to get help:
- If you have a paid Docker subscription, select **Contact support**. This opens the Docker Desktop support form. Fill in the information required and add the ID you copied in step three to the **Diagnostics ID field**. Then, select **Submit ticket** to request Docker Desktop support.
> [!NOTE]
>
> You must be signed in to Docker Desktop to access the support form. For information on what's covered as part of Docker Desktop support, see [Support](/manuals/desktop/troubleshoot-and-support/support.md).
- If you don't have a paid Docker subscription, select **Report a Bug** to open a new Docker Desktop issue on GitHub. Complete the information required and ensure you add the diagnostic ID you copied in step three.
### Diagnose from an error message
1. When an error message appears, select **Gather diagnostics**.
2. When the diagnostics are uploaded, Docker Desktop prints a diagnostic ID. Copy this ID.
3. Use your diagnostics ID to get help:
- If you have a paid Docker subscription, select **Contact support**. This opens the Docker Desktop support form. Fill in the information required and add the ID you copied in step three to the **Diagnostics ID field**. Then, select **Submit ticket** to request Docker Desktop support.
> [!NOTE]
>
> You must be signed in to Docker Desktop to access the support form. For information on what's covered as part of Docker Desktop support, see [Support](/manuals/desktop/troubleshoot-and-support/support.md).
- If you don't have a paid Docker subscription, you can open a new Docker Desktop issue on GitHub for [Mac](https://github.com/docker/for-mac/issues), [Windows](https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues), or [Linux](https://github.com/docker/for-linux/issues). Complete the information required and ensure you add the diagnostic ID printed in step two.
### Diagnose from the terminal
In some cases, it's useful to run the diagnostics yourself, for instance, if
Docker Desktop cannot start.
{{< tabs group="os" >}}
{{< tab name="Windows" >}}
1. Locate the `com.docker.diagnose` tool:
```console
$ C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\com.docker.diagnose.exe
```
2. Create and upload the diagnostics ID. In PowerShell, run:
```console
$ & "C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\com.docker.diagnose.exe" gather -upload
```
After the diagnostics have finished, the terminal displays your diagnostics ID and the path to the diagnostics file. The diagnostics ID is composed of your user ID and a timestamp. For example `BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051`.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Mac" >}}
1. Locate the `com.docker.diagnose` tool:
```console
$ /Applications/Docker.app/Contents/MacOS/com.docker.diagnose
```
2. Create and upload the diagnostics ID. Run:
```console
$ /Applications/Docker.app/Contents/MacOS/com.docker.diagnose gather -upload
```
After the diagnostics have finished, the terminal displays your diagnostics ID and the path to the diagnostics file. The diagnostics ID is composed of your user ID and a timestamp. For example `BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051`.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Linux" >}}
1. Locate the `com.docker.diagnose` tool:
```console
$ /opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose
```
2. Create and upload the diagnostics ID. Run:
```console
$ /opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose gather -upload
```
After the diagnostics have finished, the terminal displays your diagnostics ID and the path to the diagnostics file. The diagnostics ID is composed of your user ID and a timestamp. For example `BE9AFAAF-F68B-41D0-9D12-84760E6B8740/20190905152051`.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< /tabs >}}
To view the contents of the diagnostic file:
{{< tabs group="os" >}}
{{< tab name="Windows" >}}
1. Unzip the file. In PowerShell, copy and paste the path to the diagnostics file into the following command and then run it. It should be similar to the following example:
```powershell
$ Expand-Archive -LiteralPath "C:\Users\testUser\AppData\Local\Temp\5DE9978A-3848-429E-8776-950FC869186F\20230607101602.zip" -DestinationPath "C:\Users\testuser\AppData\Local\Temp\5DE9978A-3848-429E-8776-950FC869186F\20230607101602"
```
2. Open the file in your preferred text editor. Run:
```powershell
$ code <path-to-file>
```
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Mac" >}}
Run:
```console
$ open /tmp/<your-diagnostics-ID>.zip
```
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Linux" >}}
Run:
```console
$ unzip –l /tmp/<your-diagnostics-ID>.zip
```
{{< /tab >}}
{{< /tabs >}}
#### Use your diagnostics ID to get help
If you have a paid Docker subscription, select **Contact support**. This opens the Docker Desktop support form. Fill in the information required and add the ID you copied in step three to the **Diagnostics ID field**. Then, select **Submit ticket** to request Docker Desktop support.
If you don't have a paid Docker subscription, create an issue on GitHub:
- [For Linux](https://github.com/docker/desktop-linux/issues)
- [For Mac](https://github.com/docker/for-mac/issues)
- [For Windows](https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues)
### Self-diagnose tool
Docker Desktop contains a self-diagnose tool which can help you identify some common problems.
{{< tabs group="os" >}}
{{< tab name="Windows" >}}
1. Locate the `com.docker.diagnose` tool.
```console
$ C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\com.docker.diagnose.exe
```
2. In PowerShell, run the self-diagnose tool:
```console
$ & "C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\com.docker.diagnose.exe" gather
```
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Mac" >}}
1. Locate the `com.docker.diagnose` tool.
```console
$ /Applications/Docker.app/Contents/MacOS/com.docker.diagnose
```
2. Run the self-diagnose tool:
```console
$ /Applications/Docker.app/Contents/MacOS/com.docker.diagnose gather
```
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Linux" >}}
1. Locate the `com.docker.diagnose` tool.
2. Run the self-diagnose tool:
```console
$ /opt/docker-desktop/bin/com.docker.diagnose gather
```
{{< /tab >}}
{{< /tabs >}}
The tool runs a suite of checks and displays **PASS** or **FAIL** next to each check. If there are any failures, it highlights the most relevant at the end of the report.
You can then create an issue on GitHub:
- [For Linux](https://github.com/docker/desktop-linux/issues)
- [For Mac](https://github.com/docker/for-mac/issues)
- [For Windows](https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues)
## Check the logs
In addition to using the diagnose option to submit logs, you can browse the logs yourself.
{{< tabs group="os" >}}
{{< tab name="Windows" >}}
In PowerShell, run:
```powershell
$ code $Env:LOCALAPPDATA\Docker\log
```
This opens up all the logs in your preferred text editor for you to explore.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Mac" >}}
### From terminal
To watch the live flow of Docker Desktop logs in the command line, run the following script from your preferred shell.
```console
$ pred='process matches ".*(ocker|vpnkit).*" || (process in {"taskgated-helper", "launchservicesd", "kernel"} && eventMessage contains[c] "docker")'
$ /usr/bin/log stream --style syslog --level=debug --color=always --predicate "$pred"
```
Alternatively, to collect the last day of logs (`1d`) in a file, run:
```console
$ /usr/bin/log show --debug --info --style syslog --last 1d --predicate "$pred" >/tmp/logs.txt
```
### From the Console app
Mac provides a built-in log viewer, named **Console**, which you can use to check
Docker logs.
The Console lives in `/Applications/Utilities`. You can search for it with
Spotlight Search.
To read the Docker app log messages, type `docker` in the Console window search bar and press Enter. Then select `ANY` to expand the drop-down list next to your `docker` search entry, and select `Process`.
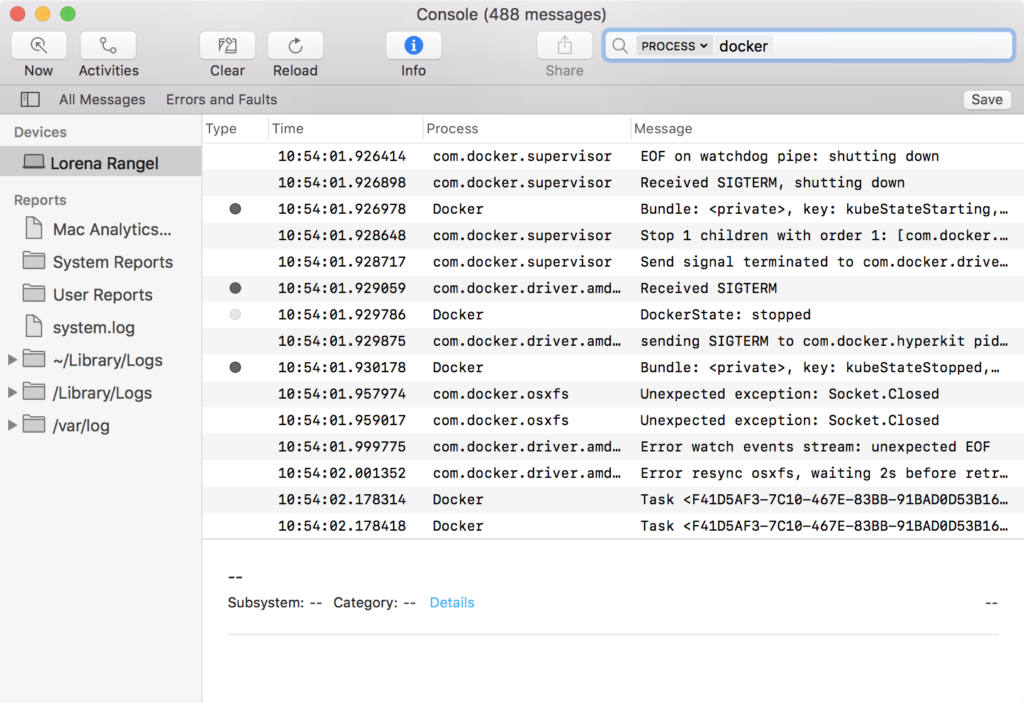
You can use the Console Log Query to search logs, filter the results in various
ways, and create reports.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="Linux" >}}
You can access Docker Desktop logs by running the following command:
```console
$ journalctl --user --unit=docker-desktop
```
You can also find the logs for the internal components included in Docker
Desktop at `$HOME/.docker/desktop/log/`.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< /tabs >}}
## View the Docker daemon logs
Refer to the [Read the daemon logs](/manuals/engine/daemon/logs.md) section
to learn how to view the Docker Daemon logs.
## Further resources
- View specific [troubleshoot topics](topics.md).
- View information on [known issues](known-issues.md)