---
description: Explore common troubleshooting topics for Docker Desktop
keywords: Linux, Mac, Windows, troubleshooting, topics, Docker Desktop
title: Troubleshoot topics for Docker Desktop
linkTitle: Common topics
toc_max: 3
tags: [ Troubleshooting ]
weight: 10
aliases:
- /desktop/troubleshoot/topics/
- /manuals/desktop/troubleshoot-and-support/troubleshoot/workarounds/
---
> [!TIP]
>
> If you do not find a solution in troubleshooting, browse the GitHub repositories or create a new issue:
>
> - [docker/for-mac](https://github.com/docker/for-mac/issues)
> - [docker/for-win](https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues)
> - [docker/for-linux](https://github.com/docker/for-linux/issues)
## Topics for all platforms
### Certificates not set up correctly
#### Error message
When attempting to pull from a registry using `docker run`, you may encounter the following error:
```console
Error response from daemon: Get http://192.168.203.139:5858/v2/: malformed HTTP response "\x15\x03\x01\x00\x02\x02"
```
Additionally, logs from the registry may show:
```console
2017/06/20 18:15:30 http: TLS handshake error from 192.168.203.139:52882: tls: client didn't provide a certificate
2017/06/20 18:15:30 http: TLS handshake error from 192.168.203.139:52883: tls: first record does not look like a TLS handshake
```
#### Possible causes
- Docker Desktop ignores certificates listed under insecure registries.
- Client certificates are not sent to insecure registries, causing handshake failures.
#### Solution
- Ensure that your registry is properly configured with valid SSL certificates.
- If your registry is self-signed, configure Docker to trust the certificate by adding it to Docker’s certificates directory (/etc/docker/certs.d/ on Linux).
- If the issue persists, check your Docker daemon configuration and enable TLS authentication.
### Docker Desktop's UI appears green, distorted, or has visual artifacts
#### Cause
Docker Desktop uses hardware-accelerated graphics by default, which may cause problems for some GPUs.
#### Solution
Disable hardware acceleration:
1. Edit Docker Desktop's `settings-store.json` file (or `settings.json` for Docker Desktop versions 4.34 and earlier). You can find this file at:
- Mac: `~/Library/Group Containers/group.com.docker/settings-store.json`
- Windows: `C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Roaming\Docker\settings-store.json`
- Linux: `~/.docker/desktop/settings-store.json.`
2. Add the following entry:
```JSON
$ "disableHardwareAcceleration": true
```
3. Save the file and restart Docker Desktop.
### Using mounted volumes and getting runtime errors indicating an application file is not found, access to a volume mount is denied, or a service cannot start
#### Cause
If your project directory is located outside your home directory (`/home/<user>`), Docker Desktop requires file sharing permissions to access it.
#### Solution
Enable file sharing in Docker Desktop for Mac and Linux:
1. Navigate to **Settings**, select **Resources** and then **File sharing**.
2. Add the drive or folder that contains the Dockerfile and volume mount paths.
Enable file sharing in Docker Desktop for Windows:
1. From **Settings**, select **Shared Folders**.
2. Share the folder that contains the Dockerfile and volume mount paths.
### `port already allocated` errors
#### Error message
When starting a container, you may see an error like:
```text
Bind for 0.0.0.0:8080 failed: port is already allocated
```
Or
```text
listen tcp:0.0.0.0:8080: bind: address is already in use
```
#### Cause
- Another application on your system is already using the specified port.
- A previously running container was not stopped properly and is still bound to the port.
#### Solution
To discover the identity of this software, either:
- Use the `resmon.exe` GUI, select **Network** and then **Listening Ports**
- In PowerShell, use `netstat -aon | find /i "listening "` to discover the PID of the process
currently using the port (the PID is the number in the rightmost column).
Then, decide whether to shut the other process down, or to use a different port in your
Docker app.
## Topics for Linux and Mac
### Docker Desktop fails to start on Mac or Linux platforms
#### Error message
Docker fails to start due to Unix domain socket path length limitations:
```console
[vpnkit-bridge][F] listen unix <HOME>/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker/Data/http-proxy-control.sock: bind: invalid argument
```
```console
[com.docker.backend][E] listen(vsock:4099) failed: listen unix <HOME>/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker/Data/vms/0/00000002.00001003: bind: invalid argument
```
#### Cause
On Mac and Linux, Docker Desktop creates Unix domain sockets used for inter-process communication. These sockets are created under the user's home directory.
Unix domain sockets have a maximum path length:
- 104 characters on Mac
- 108 characters on Linux
If your home directory path is too long, Docker Desktop fails to create necessary sockets.
#### Solution
Ensure your username is short enough to keep paths within the allowed limit:
- Mac: Username should be ≤ 33 characters
- Linux: Username should be ≤ 55 characters
## Topics for Mac
### Upgrade requires administrator privileges
#### Cause
On macOS, users without administrator privileges cannot perform in-app upgrades from the Docker Desktop Dashboard.
#### Solution
> [!IMPORTANT]
>
> Do not uninstall the current version before upgrading. Doing so deletes all local Docker containers, images, and volumes.
To upgrade Docker Desktop:
- Ask an administrator to install the newer version over the existing one.
- Use the []`--user` install flag](/manuals/desktop/setup/install/mac-install.md#security-and-access) if appropriate for your setup.
### Persistent notification telling me an application has changed my Desktop configurations
#### Cause
You receive this notification because the Configuration integrity check feature has detected that a third-party application has altered your Docker Desktop configuration. This usually happens due to incorrect or missing symlinks. The notification ensures you are aware of these changes so you can review and repair any potential issues to maintain system reliability.
Opening the notification presents a pop-up window which provides detailed information about the detected integrity issues.
#### Solution
If you choose to ignore the notification, it will be shown again only at the next Docker Desktop startup. If you choose to repair your configuration, you won't be prompted again.
If you want to switch off Configuration integrity check notifications, navigate to Docker Desktop's settings and in the **General** tab, clear the **Automatically check configuration** setting.
### `com.docker.vmnetd` is still running after I quit the app
The privileged helper process `com.docker.vmnetd` is started by `launchd` and
runs in the background. The process does not consume any resources unless
`Docker.app` connects to it, so it's safe to ignore.
### Incompatible CPU detected
#### Cause
Docker Desktop requires a processor (CPU) that supports virtualization and, more
specifically, the [Apple Hypervisor
framework](https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/DriversKernelHardware/Reference/Hypervisor/).
#### Solution
Check that:
- You've installed the correct Docker Desktop for your architecture
- Your Mac supports Apple's Hypervisor framework. To check if your Mac supports the Hypervisor framework, run the following command in a terminal window.
```console
$ sysctl kern.hv_support
```
If your Mac supports the Hypervisor Framework, the command prints `kern.hv_support: 1`.
If not, the command prints `kern.hv_support: 0`.
See also, [Hypervisor Framework
Reference](https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/DriversKernelHardware/Reference/Hypervisor/)
in the Apple documentation, and Docker Desktop [Mac system requirements](/manuals/desktop/setup/install/mac-install.md#system-requirements).
### VPNKit keeps breaking
#### Cause
In Docker Desktop version 4.19, gVisor replaced VPNKit to enhance the performance of VM networking when using the Virtualization framework on macOS 13 and later.
#### Solution
To continue using VPNKit:
1. Open your `settings-store.json` file located at `~/Library/Group Containers/group.com.docker/settings-store.json`
2. Add:
```JSON
$ "networkType":"vpnkit"
```
3. Save the file and restart Docker Desktop.
## Topics for Windows
### Docker Desktop fails to start when anti-virus software is installed
#### Cause
Some anti-virus software may be incompatible with Hyper-V and Microsoft
Windows 10 builds. The conflict
typically occurs after a Windows update and
manifests as an error response from the Docker daemon and a Docker Desktop start failure.
#### Solution
For a temporary workaround, uninstall the anti-virus software, or
add Docker to the exclusions/exceptions in your antivirus software.
### Permissions errors on data directories for shared volumes
#### Cause
When sharing files from Windows, Docker Desktop sets permissions on [shared volumes](/manuals/desktop/settings-and-maintenance/settings.md#file-sharing)
to a default value of [0777](https://chmodcommand.com/chmod-0777/)
(`read`, `write`, `execute` permissions for `user` and for `group`).
The default permissions on shared volumes are not configurable.
#### Solution
If you are
working with applications that require different permissions, either:
- Use non-host-mounted volumes
- Find a way to make the applications work with the default file permissions
### Unexpected syntax errors, use Unix style line endings for files in containers
#### Cause
Docker containers expect Unix-style line `\n` endings, not Windows style: `\r\n`. This includes files referenced at the command line for builds and in RUN commands in Docker files.
Keep this in mind when authoring files such as shell scripts using Windows
tools, where the default is likely to be Windows style line endings. These
commands ultimately get passed to Unix commands inside a Unix based container
(for example, a shell script passed to `/bin/sh`). If Windows style line endings
are used, `docker run` fails with syntax errors.
#### Solution
- Convert files to Unix-style line endings using:
```console
$ dos2unix script.sh
```
- In VS Code, set line endings to `LF` (Unix) instead of `CRLF` (Windows).
### Path conversion errors on Windows
#### Cause
Unlike Linux, Windows requires explicit path conversion for volume mounting.
On Linux, the system takes care of mounting a path to another path. For example, when you run the following command on Linux:
```console
$ docker run --rm -ti -v /home/user/work:/work alpine
```
It adds a `/work` directory to the target container to mirror the specified path.
#### Solution
Update the source path. For example, if you are using
the legacy Windows shell (`cmd.exe`), you can use the following command:
```console
$ docker run --rm -ti -v C:\Users\user\work:/work alpine
```
This starts the container and ensures the volume becomes usable. This is possible because Docker Desktop detects
the Windows-style path and provides the appropriate conversion to mount the directory.
Docker Desktop also allows you to use Unix-style path to the appropriate format. For example:
```console
$ docker run --rm -ti -v /c/Users/user/work:/work alpine ls /work
```
### Docker commands failing in Git Bash
#### Error message
```console
$ docker run --rm -ti -v C:\Users\user\work:/work alpine
docker: Error response from daemon: mkdir C:UsersUserwork: Access is denied.
```
```console
$ docker run --rm -ti -v $(pwd):/work alpine
docker: Error response from daemon: OCI runtime create failed: invalid mount {Destination:\Program Files\Git\work Type:bind Source:/run/desktop/mnt/host/c/Users/user/work;C Options:[rbind rprivate]}: mount destination \Program Files\Git\work not absolute: unknown.
```
#### Cause
Git Bash (or MSYS) provides a Unix-like environment on Windows. These tools apply their own
preprocessing on the command line.
This affects `$(pwd)`, colon-separated paths, and tilde (`~`)
Also, the `\` character has a special meaning in Git Bash.
#### Solution
- Disable Git Bash path conversion temporarily. For example, run the command with MSYS path conversion disable:
```console
$ MSYS_NO_PATHCONV=1 docker run --rm -ti -v $(pwd):/work alpine
```
- Use proper path formatting:
- Use double forward and backslashes (`\\` `//`) instead of single (`\` `/`).
- If referencing `$(pwd)`, add an extra `/`:
Portability of the scripts is not affected as Linux treats multiple `/` as a single entry.
### Docker Desktop fails due to Virtualization not working
#### Error message
A typical error message is "Docker Desktop - Unexpected WSL error" mentioning the error code
`Wsl/Service/RegisterDistro/CreateVm/HCS/HCS_E_HYPERV_NOT_INSTALLED`. Manually executing `wsl` commands
also fails with the same error code.
#### Cause
- Virtualization settings are disabled in the BIOS.
- Windows Hyper-V or WSL 2 components are missing.
Note some third-party software such as Android emulators will disable Hyper-V on install.
#### Solutions
Your machine must have the following features for Docker Desktop to function correctly:
##### WSL 2 and Windows Home
1. Virtual Machine Platform
2. [Windows Subsystem for Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10)
3. [Virtualization enabled in the BIOS](https://support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/enable-virtualization-on-windows-c5578302-6e43-4b4b-a449-8ced115f58e1)
Note that many Windows devices already have virtualization enabled, so this may not apply.
4. Hypervisor enabled at Windows startup

It must be possible to run WSL 2 commands without error, for example:
```console
PS C:\users\> wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Ubuntu Running 2
docker-desktop Stopped 2
PS C:\users\> wsl -d docker-desktop echo WSL 2 is working
WSL 2 is working
```
If the features are enabled but the commands are not working, first check [Virtualization is turned on](#virtualization-must-be-turned-on)
then [enable the Hypervisor at Windows startup](#hypervisor-enabled-at-windows-startup) if required. If running Docker
Desktop in a Virtual Machine, ensure [the hypervisor has nested virtualization enabled](#turn-on-nested-virtualization).
##### Hyper-V
On Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise, you can also use Hyper-V with the following features enabled:
1. [Hyper-V](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/virtualization/hyper-v/hyper-v-technology-overview)
installed and working
2. [Virtualization enabled in the BIOS](https://support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/enable-virtualization-on-windows-c5578302-6e43-4b4b-a449-8ced115f58e1)
Note that many Windows devices already have virtualization enabled, so this may not apply.
3. Hypervisor enabled at Windows startup
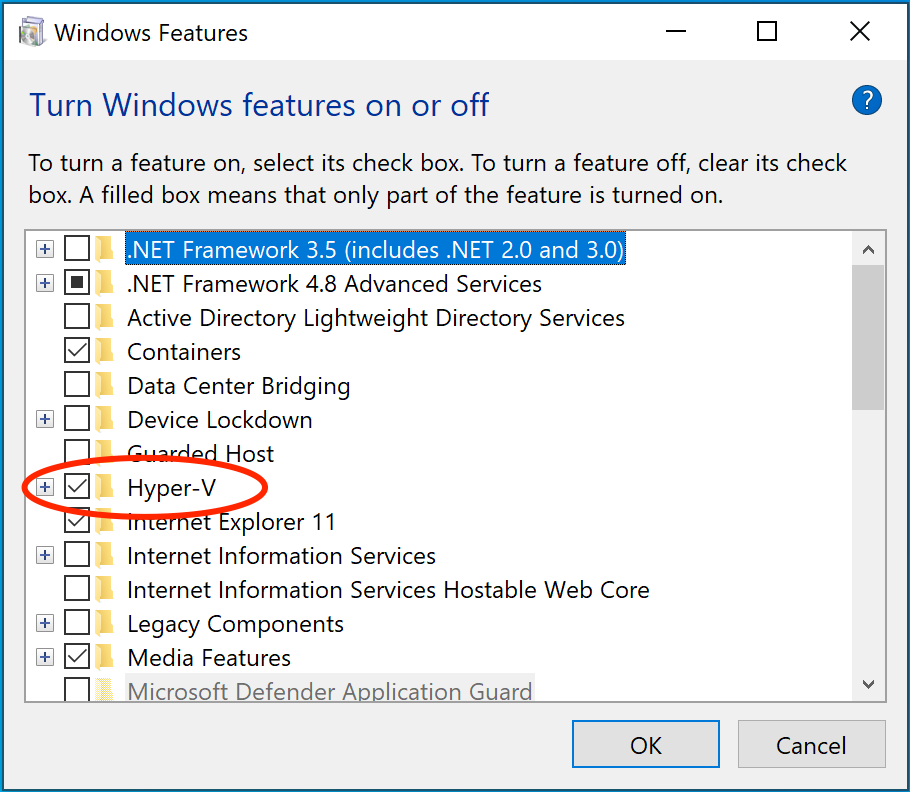
Docker Desktop requires Hyper-V as well as the Hyper-V Module for Windows
PowerShell to be installed and enabled. The Docker Desktop installer enables
it for you.
Docker Desktop also needs two CPU hardware features to use Hyper-V: Virtualization and Second Level Address Translation (SLAT), which is also called Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI). On some systems, Virtualization must be enabled in the BIOS. The steps required are vendor-specific, but typically the BIOS option is called `Virtualization Technology (VTx)` or something similar. Run the command `systeminfo` to check all required Hyper-V features. See [Pre-requisites for Hyper-V on Windows 10](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyper-v-on-windows/reference/hyper-v-requirements) for more details.
To install Hyper-V manually, see [Install Hyper-V on Windows 10](https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyperv_on_windows/quick_start/walkthrough_install). A reboot is *required* after installation. If you install Hyper-V without rebooting, Docker Desktop does not work correctly.
From the start menu, type **Turn Windows features on or off** and press enter.
In the subsequent screen, verify that Hyper-V is enabled.
##### Virtualization must be turned on
In addition to [Hyper-V](#hyper-v) or [WSL 2](/manuals/desktop/features/wsl/_index.md), virtualization must be turned on. Check the
Performance tab on the Task Manager. Alternatively, you can type `systeminfo` into your terminal. If you see `Hyper-V Requirements: A hypervisor has been detected. Features required for Hyper-V will not be displayed`, then virtualization is enabled.
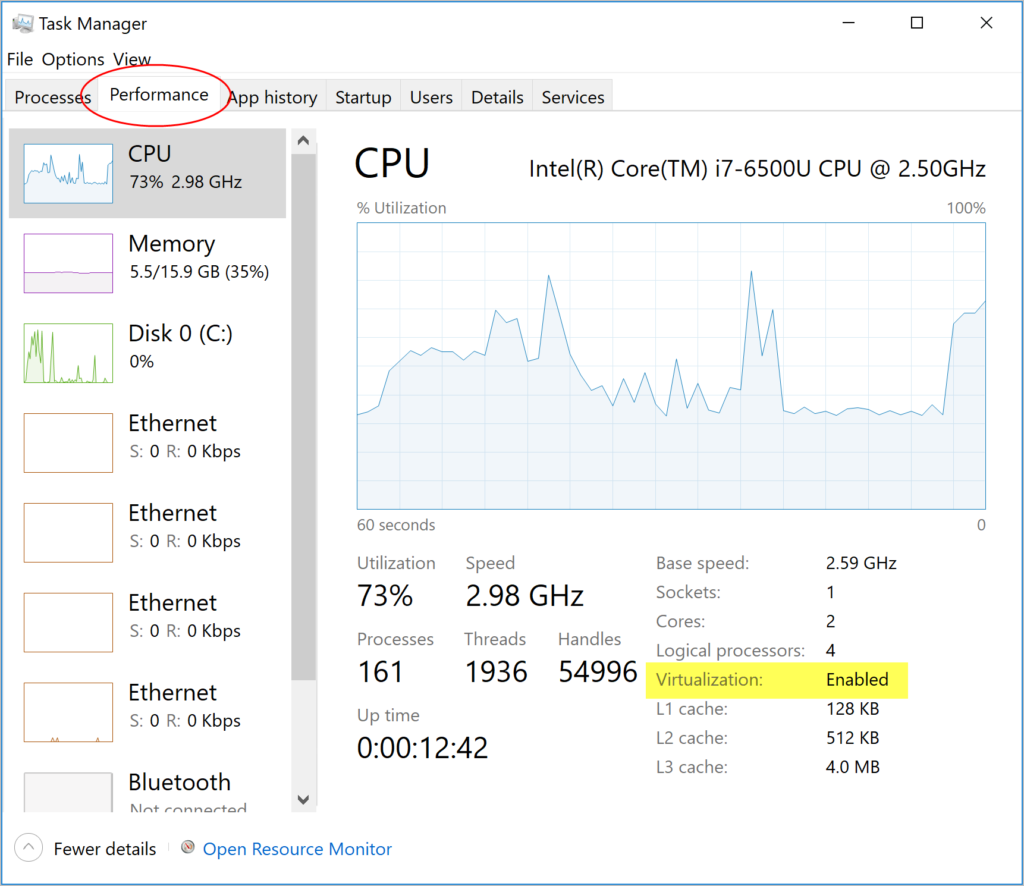
If you manually uninstall Hyper-V, WSL 2 or turn off virtualization,
Docker Desktop cannot start.
To turn on nested virtualization, see [Run Docker Desktop for Windows in a VM or VDI environment](/manuals/desktop/setup/vm-vdi.md#turn-on-nested-virtualization).
##### Hypervisor enabled at Windows startup
If you have completed the previous steps and are still experiencing
Docker Desktop startup issues, this could be because the Hypervisor is installed,
but not launched during Windows startup. Some tools (such as older versions of
Virtual Box) and video game installers turn off hypervisor on boot. To turn it back on:
1. Open an administrative console prompt.
2. Run `bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype auto`.
3. Restart Windows.
You can also refer to the [Microsoft TechNet article](https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/ee5b1d6b-09e2-49f3-a52c-820aafc316f9/hyperv-doesnt-work-after-upgrade-to-windows-10-1809?forum=win10itprovirt) on Code flow guard (CFG) settings.
##### Turn on nested virtualization
If you are using Hyper-V and you get the following error message when running Docker Desktop in a VDI environment:
```console
The Virtual Machine Management Service failed to start the virtual machine 'DockerDesktopVM' because one of the Hyper-V components is not running
```
Try [enabling nested virtualization](/manuals/desktop/setup/vm-vdi.md#turn-on-nested-virtualization).
### `Docker Desktop Access Denied` error message when starting Docker Desktop
#### Error message
When starting Docker Desktop, the following error appears:
```text
Docker Desktop - Access Denied
```
#### Cause
The user is not part of the `docker-users` group, which is required for permissions.
#### Solution
If your admin account is different to your user account, add it:
1. Run **Computer Management** as an administrator.
2. Navigate to **Local Users and Groups** > **Groups** > **docker-users**.
3. Right-click to add the user to the group.
4. Sign out and sign back in for the changes to take effect