# Stdout, Stderr, and Exit Codes
An important piece of interop between Nushell and external commands is working with the standard streams of data coming from the external.
The first of these important streams is stdout.
## Stdout
Stdout is the way that most external apps will send data into the pipeline or to the screen. Data sent by an external app to its stdout is received by Nushell by default if it's part of a pipeline:
```nu
external | str join
```
The above would call the external named `external` and would redirect the stdout output stream into the pipeline. With this redirection, Nushell can then pass the data to the next command in the pipeline, here [`str join`](/commands/docs/str_join.md).
Without the pipeline, Nushell will not do any redirection, allowing it to print directly to the screen.
## Stderr
Another common stream that external applications often use to print error messages is stderr. By default, Nushell does not do any redirection of stderr, which means that by default it will print to the screen.
## Exit Code
Finally, external commands have an "exit code". These codes help give a hint to the caller whether the command ran successfully.
Nushell tracks the last exit code of the recently completed external in one of two ways. The first way is with the `LAST_EXIT_CODE` environment variable.
```nu
do { external }
$env.LAST_EXIT_CODE
```
The second way is to use the [`complete`](/commands/docs/complete.md) command.
## Using the [`complete`](/commands/docs/complete.md) command
The [`complete`](/commands/docs/complete.md) command allows you to run an external to completion, and gather the stdout, stderr, and exit code together in one record.
If we try to run the external `cat` on a file that doesn't exist, we can see what [`complete`](/commands/docs/complete.md) does with the streams, including the redirected stderr:
```nu
cat unknown.txt | complete
# => ╭───────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────╮
# => │ stdout │ │
# => │ stderr │ cat: unknown.txt: No such file or directory │
# => │ exit_code │ 1 │
# => ╰───────────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────╯
```
## `echo`, `print`, and `log` commands
The [`echo`](/commands/docs/echo.md) command is mainly for _pipes_. It returns its arguments, ignoring the piped-in value. There is usually little reason to use this over just writing the values as-is.
In contrast, the [`print`](/commands/docs/print.md) command prints the given values to stdout as plain text. It can be used to write to standard error output, as well. Unlike [`echo`](/commands/docs/echo.md), this command does not return any value (`print | describe` will return "nothing"). Since this command has no output, there is no point in piping it with other commands.
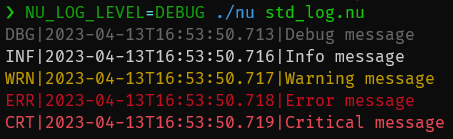
The [standard library](/book/standard_library.md) has commands to write out messages in different logging levels. For example:
@[code](@snippets/book/std_log.nu)