> [!WARNING]
>
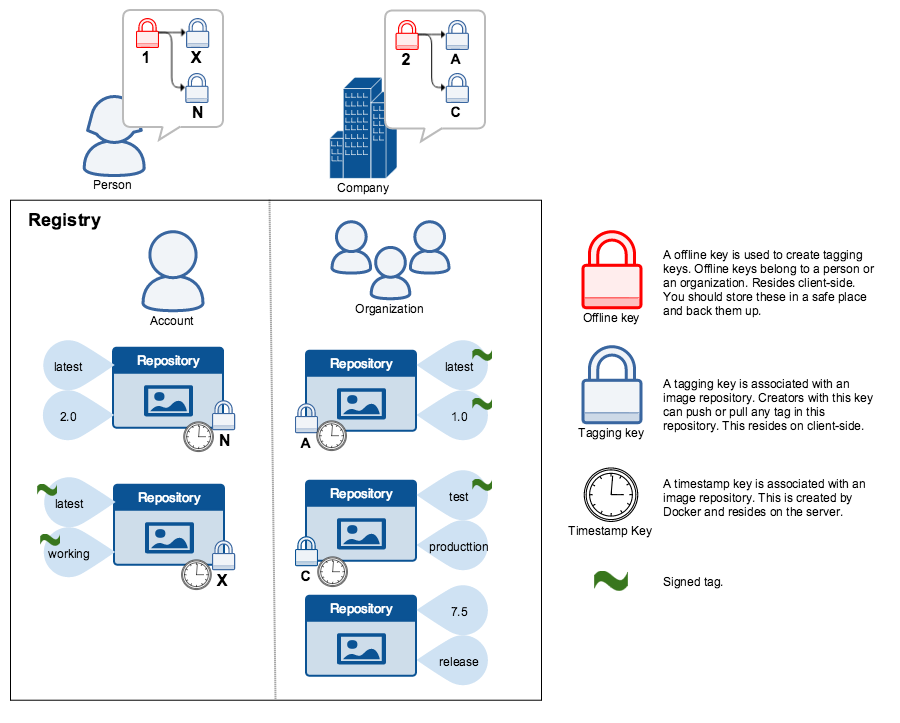
>The root key once lost is not recoverable. If you lose any other key, send an email to [Docker Hub Support](mailto:hub-support@docker.com). This loss also requires manual intervention from every
consumer that used a signed tag from this repository prior to the loss.
You should back up the root key somewhere safe. Given that it is only required
to create new repositories, it is a good idea to store it offline in hardware.
For details on securing, and backing up your keys, make sure you
read how to [manage keys for DCT](trust_key_mng.md).
## Signing images with Docker Content Trust
Within the Docker CLI we can sign and push a container image with the
`$ docker trust` command syntax. This is built on top of the Notary feature
set. For more information, see the [Notary GitHub repository](https://github.com/theupdateframework/notary).
A prerequisite for signing an image is a Docker Registry with a Notary server
attached (Such as the Docker Hub ). Instructions for
standing up a self-hosted environment can be found [here](/engine/security/trust/deploying_notary/).
To sign a Docker Image you will need a delegation key pair. These keys
can be generated locally using `$ docker trust key generate` or generated
by a certificate authority.
First we will add the delegation private key to the local Docker trust
repository. (By default this is stored in `~/.docker/trust/`). If you are
generating delegation keys with `$ docker trust key generate`, the private key
is automatically added to the local trust store. If you are importing a separate
key, you will need to use the
`$ docker trust key load` command.
```console
$ docker trust key generate jeff
Generating key for jeff...
Enter passphrase for new jeff key with ID 9deed25:
Repeat passphrase for new jeff key with ID 9deed25:
Successfully generated and loaded private key. Corresponding public key available: /home/ubuntu/Documents/mytrustdir/jeff.pub
```
Or if you have an existing key:
```console
$ docker trust key load key.pem --name jeff