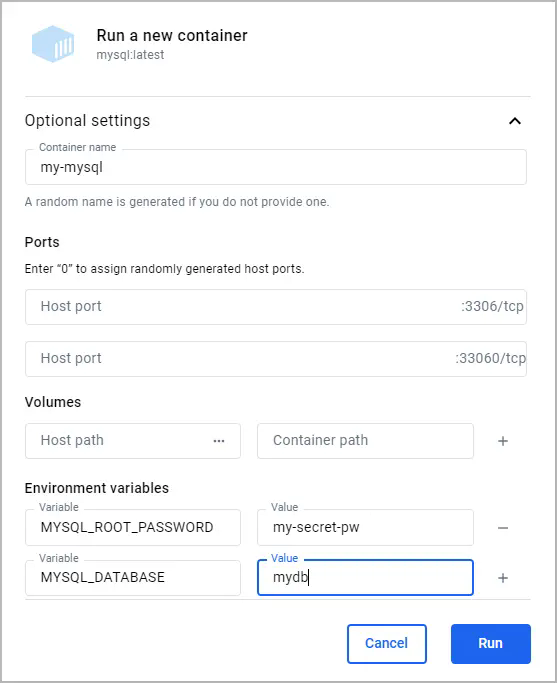
6. Select `Run`.
7. Open the **Container** view in the Docker Desktop Dashboard to verify that your
container is running.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< /tabs >}}
## Access the shell of a containerized database
When you have a database running inside a Docker container, you may need to
access its shell to manage the database, execute commands, or perform
administrative tasks. Docker provides a straightforward way to do this using the
`docker exec` command. Additionally, if you prefer a graphical interface, you
can use Docker Desktop's GUI.
If you don't yet have a database container running, see
[Run a local containerized database](#run-a-local-containerized-database).
{{< tabs group="ui" >}}
{{< tab name="CLI" >}}
To access the terminal of a MySQL container using the CLI, you can use the
following `docker exec` command.
```console
$ docker exec -it my-mysql bash
```
In this command:
- `docker exec` tells Docker you want to execute a command in a running
container.
- `-it` ensures that the terminal you're accessing is interactive, so you can
type commands into it.
- `my-mysql` is the name of your MySQL container. If you named your container
differently when you ran it, use that name instead.
- `bash` is the command you want to run inside the container. It opens up a bash
shell that lets you interact with the container's file system and installed
applications.
After executing this command, you will be given access to the bash shell inside
your MySQL container, from which you can manage your MySQL server directly. You
can run `exit` to return to your terminal.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< tab name="GUI" >}}
1. Open the Docker Desktop Dashboard and select the **Containers** view.
2. In the **Actions** column for your container, select **Show container
actions** and then select **Open in terminal**.
In this terminal you can access to the shell inside your MySQL container, from
which you can manage your MySQL server directly.
{{< /tab >}}
{{< /tabs >}}
Once you've accessed the container's terminal, you can run any tools available